Photo credit: NASA, "Earthrise".
INTRODUCING BIOMINERALS: A NEW CLASS OF BIOFERTILIZERS
BIOMINERAL FOUNDATION NFX
A REVOLUTIONARY SOIL AMENDMENT, SOIL CONDITIONER, AND BIOFERTILIZER
Advancing the best practices of soil remineralization combining rock dusts, clays and humates with pyrogenic carbon (a.k.a., biochar) and selecting non-GMO biomass to culture abundant microbiology on mineral and carbon substrates using proprietary methods. Product Sheet > / California Label >
CALIFORNIA FIELD TRIAL AND GERMINATION REPORTS 2024 - 2025
Wheat Germination Report >
Carriere Farms Rice Report 2024>
Carriere Farms Rice Report 2025>
Carriere Farms Almond and Walnut Report 2024>
Carriere Farms Almond Report 2025>
ShoEi USA Almond Report 2024>
Pacific Farms and Orchards Prunes Report 2024>
PT Ranch Forage Hay Report 2024>
Nuss Family Farms Processing Tomatoes 2024-2025>
Need more technical information on use of Biominerals related to climate and Enhanced Weathering? See more.
Advancing the best practices of soil remineralization combining rock dusts, clays and humates with pyrogenic carbon (a.k.a., biochar) and selecting non-GMO biomass to culture abundant microbiology on mineral and carbon substrates using proprietary methods. Product Sheet > / California Label >
CALIFORNIA FIELD TRIAL AND GERMINATION REPORTS 2024 - 2025
Wheat Germination Report >
Carriere Farms Rice Report 2024>
Carriere Farms Rice Report 2025>
Carriere Farms Almond and Walnut Report 2024>
Carriere Farms Almond Report 2025>
ShoEi USA Almond Report 2024>
Pacific Farms and Orchards Prunes Report 2024>
PT Ranch Forage Hay Report 2024>
Nuss Family Farms Processing Tomatoes 2024-2025>
Need more technical information on use of Biominerals related to climate and Enhanced Weathering? See more.
BUY NOW! 35 lb. box with free shipping >
READ SOME GOOD SCIENCE FROM THE FRONT LINE OF CLIMATE TECH AND AGRICULTURE
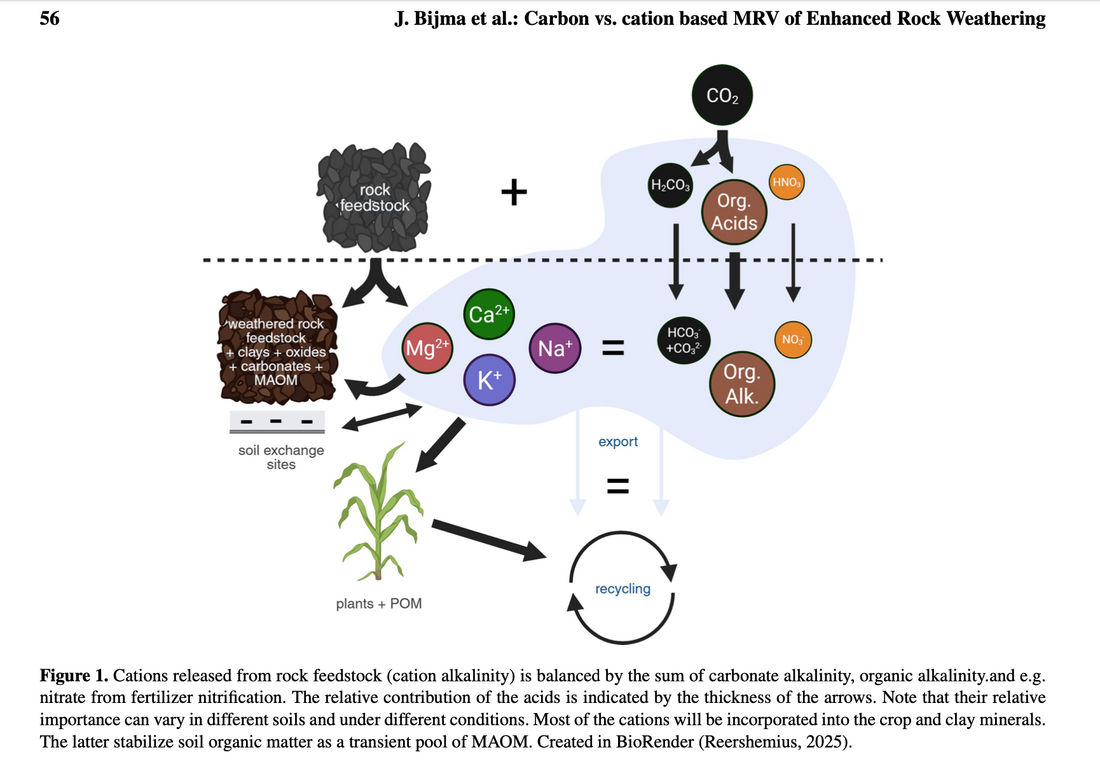
J. Bijma et al.: Carbon vs. cation based MRV of Enhanced Rock Weathering >
Excerpt:
Analogy to Terra Preta
Amazonian black earth or “terra preta” is typically associated with human occupation, but it is uncertain whether it was created intentionally. Interestingly, “terra preta” is not only characterised by its high organic carbon content and the presence of biochar but also by a high density of broken ceramic artefacts (e.g. Schmidt et al., 2023). Ancient Amazonians produced a lot of breakable pottery and the prevalence of pottery shards may be incidental and not part of a plan to improve soil fertility, but the practice of adding biochar and pottery shards to organic leftovers of manioc, cassava, corn, papaya and bananas, sequestered and stored carbon in the soil for centuries (Lima et al., 2002; Costa et al., 2004) and may demonstrate that broken pottery is an essential ingredient in terra preta analogous to clay minerals for building up SOC in arable soils (Rowley et al., 2021).
Interestingly, Anthony et al. (2025) show that the combined ground rock, compost, and biochar amendment had the greatest increases in soil C stocks over 3 years. This can be a coincidence but that composition is very similar to terra preta (except that pottery shards are replaced by crushed rock forming clay minerals). Could it be that the combination of organic amendments, biochar and crushed rock is also the best practice for CDR?
Excerpt:
Analogy to Terra Preta
Amazonian black earth or “terra preta” is typically associated with human occupation, but it is uncertain whether it was created intentionally. Interestingly, “terra preta” is not only characterised by its high organic carbon content and the presence of biochar but also by a high density of broken ceramic artefacts (e.g. Schmidt et al., 2023). Ancient Amazonians produced a lot of breakable pottery and the prevalence of pottery shards may be incidental and not part of a plan to improve soil fertility, but the practice of adding biochar and pottery shards to organic leftovers of manioc, cassava, corn, papaya and bananas, sequestered and stored carbon in the soil for centuries (Lima et al., 2002; Costa et al., 2004) and may demonstrate that broken pottery is an essential ingredient in terra preta analogous to clay minerals for building up SOC in arable soils (Rowley et al., 2021).
Interestingly, Anthony et al. (2025) show that the combined ground rock, compost, and biochar amendment had the greatest increases in soil C stocks over 3 years. This can be a coincidence but that composition is very similar to terra preta (except that pottery shards are replaced by crushed rock forming clay minerals). Could it be that the combination of organic amendments, biochar and crushed rock is also the best practice for CDR?
READ THIS > Chapter 2 of the book geotherapy, published 2015 by Tom Goreau
Introducing hiphi earth...
Introducing HiPhi Earth, a non-profit project launched in 2025 by Trevor Vaughn and a team of "Bio-Avengers" taking aim at establishing "Agri-Hoods", research centers and community based regenerative ag solutions for the future, now!
With early fiscal sponsorship provided by The Buckminster Fuller Institute (www.BFI.org), this project is melding bioregionalism, agriculture and architecture, map based data management and boots on the ground practices aimed at building climate adaptation and mitigation into the fabric of local communities. Working with First Nations, ranchers, real estate developers, manufacturers, farmers and community organizers, HiPhi Earth is inviting participation from local individuals, farmers, organizers, philanthropic organizations and technologists. To learn more, watch the video. Or get in touch with us here at Rock Dust Local. We support HiPhi Earth!
With early fiscal sponsorship provided by The Buckminster Fuller Institute (www.BFI.org), this project is melding bioregionalism, agriculture and architecture, map based data management and boots on the ground practices aimed at building climate adaptation and mitigation into the fabric of local communities. Working with First Nations, ranchers, real estate developers, manufacturers, farmers and community organizers, HiPhi Earth is inviting participation from local individuals, farmers, organizers, philanthropic organizations and technologists. To learn more, watch the video. Or get in touch with us here at Rock Dust Local. We support HiPhi Earth!